SVD, pseudoinverse, and PCA: SVD, pseudoinverse and PCA in R
 Pseudoinverse
Pseudoinverse
The pracma package in R contains the pinv function to numerically determine the pseudoinverse of a matrix.
Example 1: linear regression First we calculate the example from the lesson text:
> library(pracma) A <- matrix(c(1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3), nrow=3); A # matrix A for regression line
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 1 1
[2,] 1 2
[3,] 1 3
> b <- c(2, 2, 4) # data vector
b = 2 2 4
> Ainv <- round(pinv(A), 4); Ainv # pseudoinverse
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 1.3333 0.3333 -0.6667
[2,] -0.5000 0.0000 0.5000
> Ainv %*% b # regression coefficients
[,1]
[1,] 0.6667
[2,] 1.0000
Here is the result: \(y= 0.6667+ t\). We can also calculate the result via the singular value decomposition.
> svdA <- svd(A) # singular value decomposition of A
> U <- svdA$u; U # matrix U in SVD
[,1] [,2]
[1,] -0.3231099 0.8537759
[2,] -0.5475070 0.1832195
[3,] -0.7719042 -0.4873369
> S <- diag(svdA$d); S
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 4.079143 0.0000000
[2,] 0.000000 0.6004912
> V <- svdA$v; V
[,1] [,2]
[1,] -0.4026632 0.9153482
[2,] -0.9153482 -0.4026632
[1] -0.4026632 -0.4026632
> Splus <- inv(S); Splus
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 0.2451495 0.000000
[2,] 0.0000000 1.665303
> Ainv <- V %*% Splus %*% t(U); Ainv # pseudoinverse
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] 1.333333 3.333333e-01 -0.6666667
[2,] -0.500000 -4.163336e-17 0.5000000
> Ainv %*% b # regression coefficients
[,1]
[1,] 0.6666667
[2,] 1.0000000Example 2: Quadratic Regression The second example involves a data set that we construct by adding noise to the \(1-2x+\frac{1}{2}x^2\) parabola. Hereafter we search for the parabola that fits the created data set best. In our data set this is approximately \(y=0.95-2.06x+0.52x^2\).
> library(pracma)
> x <- seq(from=0, to=4, by=0.5)
> m <- length(x)
> y <- rep(1,m) - 2*x + x^2/2 # parabola
> y <- y + 0.1*max(y)*sample(c(-1,1), m, replace=TRUE) # 10% noise added
> A = cbind(rep(1,m), x, x^2)
> pinvA <- pinv(A)
> c <- pinvA %*% y; c # pseudoinverse of A gives regression coefficients
[,1]
[1,] 0.9545455
[2,] -2.0601732
[3,] 0.5233766
> xx <- seq(from=-0.1, to=4.1, length=50)
> yy <- rep(c[1],50) + c[2]*xx + c[3]*xx^2
> plot(x, y, type="p", col="blue", pch=1)
> lines(xx, yy, col="green", lwd=2) # visualisation of data + approximation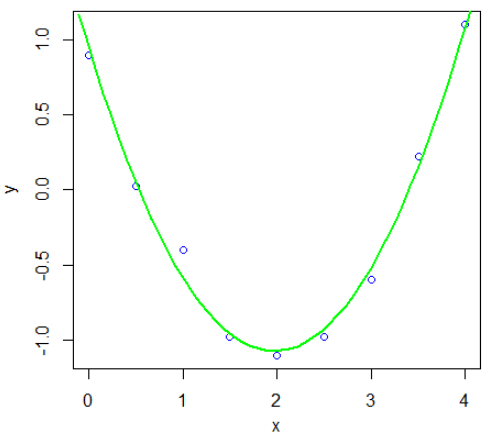
Unlock full access



