Systems of differential equations: Linear systems of differential equations
 A qualitative phase portrait
A qualitative phase portrait
We are going to see how we can use mathematical software to draw a phase portrait and solution curves. But you can also perform a qualitative analysis in which you just roughly outline in what direction a solution curve would go at a point in the phase plane.
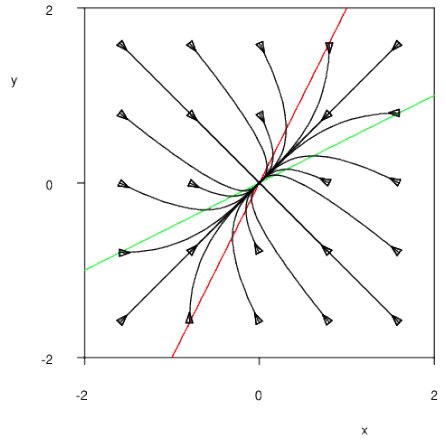
As an example we consider the system \[\left\{\begin{aligned} \frac{\dd x}{\dd t} &= -2x+ y\\[0.25cm] \frac{\dd y}{\dd t} &= x -2 y\end{aligned}\right.\] First you look at the \(x\)-nullclines and \(y\)-nullclines, that is, at the points in the \(y\)-\(x\) plane where \(\frac{\dd x}{\dd t}=0\) or \(\frac{\dd y}{\dd t}=0\), respectively . This isoclines are straight lines: \[\frac{\dd x}{\dd t} =0\iff y=2x\qquad \text{and}\qquad \frac{\dd y}{\dd t}=0\iff y=\frac{1}{2}x\] These straight lines separates the phase plane into areas in which solution curves go qualitatively in a different direction: for instance, in this example, curves move to the right on the left-hand side of the \(x\)-nullclines \((\frac{\dd x}{\dd t}>0)\) and curves move to the left on the right-hand side of the \(x\)-nullclines \((\frac{\dd x}{\dd t}<0)\); curves above the \(y\)-nullclines go downward \((\frac{\dd y}{\dd t}<0)\) and curves below the \(y\)-nullclines go upward \((\frac{\dd y}{\dd t}>0)\). This is what you see in the computer-generated phase portrait below, in which the red line forms the\(x\)-nullcline and the green line forms the \(y\)-nullcline.
In the diagram below, we have again drawn the nullclines, but no solution curves. Instead, we just indicated with arrows the directions in which a solution curve at a point would go in terms of change in \(x\) and \(y\). The resultant vectors would give the direction field.
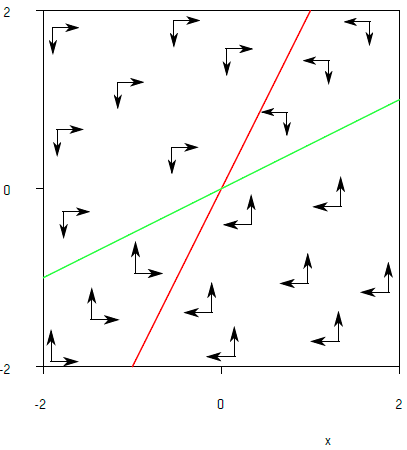
Let us look in more detail at the above diagram with separate \(x\) - and \(y\) directions, and not at resultant vectors. Then we can distinguish four cases.
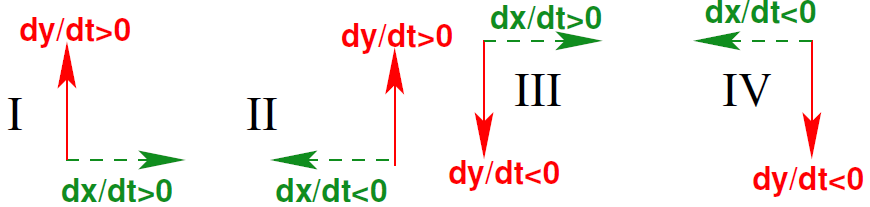
The four cases are:
- \(x\) and \(y\) increase both
- \(x\) decreases and \(y\) increases
- \(x\) increases and \(y\) decreases
- \(x\) and \(y\) decrease both
The first two cases I and II are separated by the \(x\)-nullcline and the cases I and III are separated by the \(y\)-nullcline. But the \(x\)-nullcline also separates cases III and IV. Similarly, the \(y\)-nullcline also separates cases II and IV.
In addition it is true that the direction on the line of the \(x\)-nullcline is vertical, and on the line of the \(y\)-nullcline is horizontal.
Finally we note that currently all directions in the diagram point toward the equilibrium \((0,0)\): so, all solutions go towards the origin. In other words \((0,0)\) is an attracting equilibrium in this example.


