Consider a vector quantity \(\vec{x}(t) = \cv{x_1(t)\\ x_2(t)}\) of which the change in time is given by the equation \(\frac{\dd \vec{x}}{\dd t} = A\,\vec{x}\) with matrix \[A =\matrix{-1 & 0\\ 1 & -1}\]
-
Calculate the eigenvalues and vectors of \(A\).
-
What is the formula for the solution \(\vec{x}(t)\) at any time \(t\)?
-
What are successively \(\vec{x}(1), \vec{x}(2)\), \(\vec{x}(4)\) and \(\vec{x}(8)\) when \(\vec{x}(0)=\cv{3\\2}\)?
-
What are the answers to task (c) \(\vec{x}(0)=\cv{1\\ 0}\)? Give the equation of the path in the \(y\) - \(x\) plane.
- What are the answers to task (c) \(\vec{x}(0)=\cv{0\\ 1}\)? Give the equation of the path in the \(y\) - \(x\) plane.
- Give the equation of the trajectory of a solution for an arbitrary choice \(\vec{x}(0)=\cv{\alpha \\ \beta}\)?
\(\quad\frac{\dd}{\dd t}\vec{x}=A\, \vec{x}\quad\) with \(A = \matrix{-1 & 0\\1 & -1\\}\)
- \(\quad\) The characteristic polynomial of \(A\) is because of its lower triangle form
\(\quad\)equal to \((\lambda+1)^2\)
\(\quad\)The eigenvalues of \(A\) are zeros of the characteristic polynomial: \(-1\).
\(\quad\) Let \(\cv{v_1\\ v_2}\) be an eigenvector corresponding to the eigenvalue \(-1\):
\(\quad\)\(\matrix{-1 & 0\\1 & -1\\}\cdot \cv{v_1\\ v_2}=-\cv{v_1\\ v_2}\).
\(\quad\)Then: \(\left\{\begin{aligned} -v_1 &= -v_1 \\[0.2cm] v_1-v_2 &= -v_2\end{aligned}\right.\)
\(\quad\)So: \(v_1=0\) and an eigenvector corresponding to the eigenvalue \(-1\) (with integral coefficients)
\(\quad\)is \(\vec{v}=\cv{0\\1}\).
- \(\quad\)A generalised eigenvector \(\vec{w}=\cv{w_1\\ w_2}\) corresponding to the eigenvalue \(-1\) satisfies
\(\quad\)\((A-\lambda\cdot I)\vec{w}=\vec{v}\) with \(\lambda=-1\) and \(\vec{v}=\cv{0\\ 1}\)
\(\quad\)So: \(\matrix{0 & 0\\1 & 0\\}\cdot \cv{w_1\\ w_2}=\cv{0\\ 1}\).
\(\quad\)Thus: \(w_1=1\) and \(w_2\) can be freely chosen.
\(\quad\)Take \(w_2=0\), then \(\vec{w}=\cv{1\\ 0}\) is a generalised eigenvector.
\(\quad\)The general solution is \[\begin{aligned}\vec{x}(t)&=\beta\, e^{-t}\cdot\vec{v}+ \alpha\, e^{-t}\cdot \left(t\cdot \vec{v}+\vec{w}\right) \\ \\ &= \beta\, e^{-t}\cdot\cv{0\\1}+ \alpha\, e^{-t}\cdot \left(t\cdot \cv{0\\1}+ \cv{1\\ 0}\right)\\ \\ &= \cv{\alpha\, e^{-t}\\ \beta\, e^{-t}+\alpha\, t\, e^{-t}}\end{aligned}\] \(\quad\) with constants \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\).
- \(\quad\vec{x}(0)=\cv{3\\2}\) means that \(x_1(0)=3\) and \(x_2(0)=2\).
\(\quad\)Substitution in the general solution (b) gives \(\alpha=3\) and \(\beta=2\),
\(\quad\)and thus
\(\vec{x}(t)=\cv{3e^{-t}\\ 2e^{-t}+3t e^{-t}}\).
\(\quad\)Then: \(\vec{x}(1)=\cv{3/e\\ 5/e},\quad \vec{x}(2)=\cv{3/e^2\\ 8/e^2}, \quad \vec{x}(4)=\cv{3/e^4\\ 14/e^4}, \quad \vec{x}(8)=\cv{3/e^8\\ 18/e^8}\).
- \(\quad\vec{x}(0)=\cv{1\\0}\) means that \(x_1(0)=1\) and \(x_2(0)=0\).
\(\quad\)Substitution in the general solution (b) gives \(\alpha=1\) and \(\beta=0\),
\(\quad\)and thus \(\vec{x}(t)=\cv{e^{-t}\\ t e^{-t}}\).
\(\quad\)Then: \(\vec{x}(1)=\cv{1/e\\ 1/e},\quad \vec{x}(2)=\cv{1/e^2\\ 2/e^2}, \quad \vec{x}(4)=\cv{1/e\\ 4/e^4}, \quad \vec{x}(8)=\cv{1/e^8\\ 8/e^8}\).
\(\quad\)When \(\left\{\begin{aligned} x_1 &= e^{-t}\\ x_2 &= te^{-t}\end{aligned}\right.\) then \(\ln(x_1)=-t\) and \(x_2=t\cdot x_1\) So: \(x_2=-x_1\ln(x_1)\)
- \(\quad\vec{x}(0)=\cv{0\\1}\) means that \(x_1(0)=0\) and \(x_2(0)=1\).
\(\quad\)Substitution in the general solution (b) gives \(\alpha=0\) and \(\beta=1\). \(\quad\)and thus \(\vec{x}(t)=\cv{0\\ e^{-t}}\).
\(\quad\)Then: \(\vec{x}(1)=\cv{0\\ 1/e},\quad \vec{x}(2)=\cv{0\\ 1/e^2}, \quad \vec{x}(4)=\cv{0\\ 1/e^4}, \quad \vec{x}(8)=\cv{0\\ 1/e^8}\).
\(\quad\)The orbit is \(\left\{\cv{0\\y}\,\middle\vert\, y>0\right\}\).
- \(\quad\vec{x}(0)=\cv{\alpha\\ \beta}\) means \(x_1(0)=\alpha\) and \(x_2(0)=\beta\).
\(\quad\)Substitution in the general solution (b) gives \(\vec{x}(t)=\cv{\alpha\, e^{-t}\\ \beta\, e^{-t}+\alpha\, t\, e^{-t}}\).
\(\quad\)When \(\left\{\begin{aligned} x_1 &= \alpha\, e^{-t}\\ x_2 &= \beta\, e^{-t}+\alpha\, t\, e^{-t}\end{aligned}\right.\), then generically \(t=\ln\left(\frac{\alpha}{x_1}\right)\) and \(\alpha\cdot x_2=\beta\cdot x_1 + \alpha\cdot t\cdot x_1\).
\(\quad\)The orbit has generically the equation \(\alpha \cdot x_2 =\beta\cdot x_1+\alpha\cdot x_1\cdot \ln\left(\frac{\alpha}{x_1}\right)\)
\(\quad\) 'Generically' means that we assume logarithms with a positive argument.
\(\quad\)So we consider the case \(\alpha>0\) and \(x_1>0\) and the case \(\alpha<0\) and \(x_1<0\).
\(\quad\)The case that \(\alpha=0, \beta>0\) is dealt with in (e):
\(\quad\)The trajectory is the positive vertical axis.
\(\quad\)This is illustrated in the phase portrait below.
\(\quad\)The equilibrium \((0,0)\) is attracting.
\(\quad\) 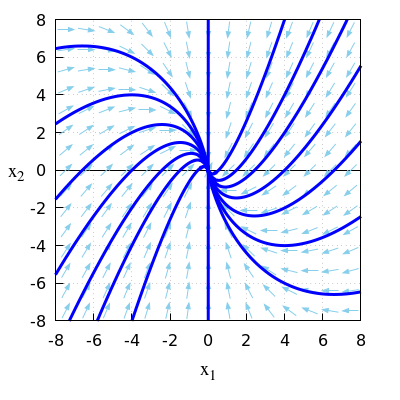
 Pencil-and-paper exercise set 2
Pencil-and-paper exercise set 2




