Multiple integrals: Double integrals
 Change of variables in double integrals
Change of variables in double integrals
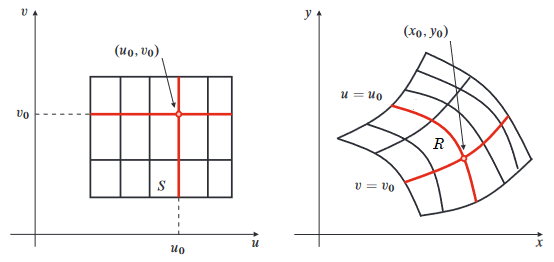
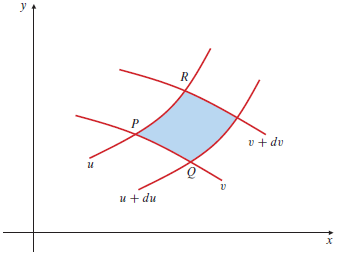
Double integral in other coordinates Suppose \(x=x(u,v)\) and \(y=y(u,v)\) is an invertible map of a region \(S\) in the \(uv\)-plane to a region \(R\) in the \(xy\)-plane and suppose the functions \(x\) and \(y\) have continuous derivatives on \(S\). If the double integral \(\displaystyle \iint_R f(x,y)\,\dd(x,y)\) exists (i.e. \(f(x,y)\) is integrable on \(R\) ) and if \(g(u,v)=f\bigl(x(u,v), y(u,v)\bigr)\), then \(g(u,v)\) is integrable on \(S\) and \[\iint_R f(x,y)\,\dd(x,y) =\iint_S g(u,v)\cdot \bigl|J(u,v)\bigr|\,\dd u\, \dd v)\] where the Jacobian \(J(u,v)\) is defined as \[\begin{aligned}J(u,v)&=\det\matrix{\dfrac{\partial x}{\partial u} &\dfrac{\partial x}{\partial v}\\ \dfrac{\partial y}{\partial u} & \dfrac{\partial y}{\partial v}}\\[0.25cm] &= \frac{\partial x}{\partial u} \cdot \frac{\partial y}{\partial v} -\frac{\partial x}{\partial v} \cdot \frac{\partial y}{\partial u}\end{aligned} \]
By the substitution \[u=x+y\quad\text{and}\quad v=x-y\] the integrand becomes a simpler expression, which is \(e^{\frac{v}{u}}\). The region of integration is mapped to a new triangle \(S\) in the \(uv\)-plane bounded by the lines \(u=v\), \(u=-v\) and \(u=1\). After all, we can isolate \(x\) and \(y\) in the above equations as \[x=\frac{1}{2}(u+v)\quad\text{and}\quad y=\frac{1}{2}(u-v)\] Therefore: \[\begin{aligned} y=-x+1&\iff u=1\\[0.25cm] x=0 &\iff u=-v\\[0.25cm] y=0 &\iff u=v\end{aligned}\] With this we then have the coordinate transformation that maps \(S\) to \(R\) in the \(xy\)-plane. The Jacobian \(J(u,v)\) can also be calculated directly: \[\begin{aligned}J(u,v) &= \det\matrix{\frac{1}{2} & \frac{1}{2}\\ \frac{1}{2} & -\frac{1}{2}}\\[0.25cm] &= -\frac{1}{2}\end{aligned}\] The calculation of the double integral now proceeds as follows: \[\begin{aligned} \iint_R e^{\frac{x-y}{x+y}}\,\dd(x,y) &= \iint_S e^{\frac{v}{u}}\,\bigl|J(u,v)\bigr|\,\dd(u,v) \\[0.25cm] &= \frac{1}{2}\int_{u=0}^{u=1}\left(\int_{v=-u}^{v=u}e^{\frac{v}{u}}\,\dd v\right)\dd u\\[0.25cm] &= \frac{1}{2}\int_{u=0}^{u=1} \biggl[u\,e^{\frac{v}{u}}\biggr]_{v=-u}^{v=u}\;\dd u\\[0.25cm] &=\frac{1}{2}\int_{u=0}^{u=1}\left(e-\frac{1}{e}\right)u\,\dd u\\[0.25cm] &= \frac{1}{2}\left(e-\frac{1}{e}\right)\cdot\biggl[\frac{1}{2}u^2\biggr]_{u=0}^{u=1}\\[0.25cm] &= \frac{1}{4}\left(e-\frac{1}{e}\right)\end{aligned}\]