4. Probability Distributions: Random Variables
 Probability Distributions
Probability Distributions
Probability Distribution
Definition
A probability distribution is a function that links each outcome#\,# of a random experiment to the probability of its occurrence.
Notation
The probability distribution of a random variable #X# is denoted by #f(x)#.
#\phantom{0}#
Discrete Variables: Probability Mass Function
The probability distribution of a discrete random variable is called the probability mass function and gives the probability that #X# equals #x#, for each #x# within the range of #X#.
\[f(x)=\mathbb{P}(X=x)\]
The cumulative distribution function of a discrete random variable gives the probability that #X# is less than or equal to #x#.
\[F(x)=\mathbb{P}(X\leq x)\]
Consider the random experiment of tossing two coins. Let #X# denote the number of Heads.
Then the probability distribution of #X# is:
| #x# | #0# | #1# | #2# |
| #\mathbb{P}(X=x)# | #0.25# | #0.5# | #0.25# |
Discrete Distribution: Important Properties
For any discrete probability distribution, the following properties hold:
- #\mathbb{P}(X \leq x) = \mathbb{P}(X=0) +\mathbb{P}(X=1) + \ldots + \mathbb{P}(X=x)#
- #\mathbb{P}(X \geq x) = 1 - \mathbb{P}(X \lt x) = 1 - \mathbb{P}(X \leq x-1)#
- #\mathbb{P}(X \lt x) = \mathbb{P}(X \leq x-1) = 1 - \mathbb{P}(X \geq x)#
- #\mathbb{P}(X \gt x) = \mathbb{P}(X \geq x+1) = 1 - \mathbb{P}(X \leq x)#
Additionally, for any #2# values #a# and #b# in the range of #X# (with #a<b#):
- #\mathbb{P}(a \lt X \leq b) = \mathbb{P}(X \leq b) - \mathbb{P}(X \leq a)#
#\phantom{0}#
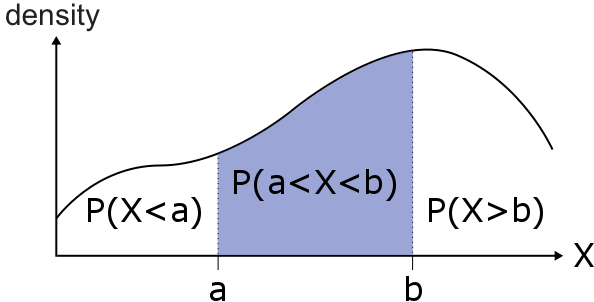
Continuous Variables: Probability Density Function
The probability distribution of a continuous random variable is called the probability density function.
The probability that a random variable #X# lies between #a# and #b# is given by the area under the curve
from #a# to #b#.
#\phantom{0}#
Continuous Distribution: Important Properties
For any continuous probability distribution, the following properties always hold:
- #\mathbb{P}(X=k)=0#
- #\mathbb{P}(X\leq k)=\mathbb{P}(X\lt k) =1 - \mathbb{P}(X \geq k)#
- #\mathbb{P}(X\geq k)=\mathbb{P}(X\gt k)= 1 - \mathbb{P}(X \leq k)#
Additionally, for any #2# numbers #j# and #k# (with #j\lt k#), the following properties hold:
-
#\mathbb{P}(j\lt X\lt k)=\mathbb{P}(j\leq X \lt k)=\mathbb{P}(j \lt X\leq k)=\mathbb{P}(j\leq X\leq k)#
- #\mathbb{P}(k\gt X \gt j)=\mathbb{P}(k\geq X \gt j)=\mathbb{P}(k\gt X\geq j)=\mathbb{P}(k \geq X\geq j)#
- #\mathbb{P}(j \leq X \leq k) = \mathbb{P}(X \leq k) - \mathbb{P}(X \leq j)#



