Solving equations and inequalities: Linear inequalities in one unknown
 Solving a linear inequality via equations
Solving a linear inequality via equations
You can also solve a linear inequality by
- first replacing the inequality sign by an equal sign,
- then solving this equation, and
- finally, determining the sign of the inequality for point to the left and to the right of the solution of the equation.
Determine the exact solution of the inequality \[-2x + 4 \ge -x {\,+\,}7\] via equations.
\(x \le -3\)
We follow the following roadmap:
- Get started with the corresponding equation \[-2x + 4 = -x {\,+\,}7\]
- Solve this equation:
- Get the terms with \(x\) on the left-hand side of the equation (by adding \(x\) on both sides):
\(-2x + 4 +x = -x {\,+\,}7 +x\), which simplifies to \(-x +4 = 7\). - Then move the terms without \(x\) to the right (by adding \(-4\) both sides):
\(-x +4 - 4 = 7 - 4\), which simplifies to \(-x = 3\).- Next, divide the left- and right-hand side by the coefficient of \(x\) (which is here \(-1\)); this gives \(x = \;\frac{3}{-1}\).
- So, the solution of the equation is \(x = {-3}\).
- Get the terms with \(x\) on the left-hand side of the equation (by adding \(x\) on both sides):
- Find out whether the solutions are on the number line to the left or to the right of \(-3\).
- First calculate the left- and right-hand sides of the inequality \(-2x + 4 \ge -x {\,+\,}7\) when you substitute a value of \(x\) less than or equal to \(-3\). For example, when you fill in \(x=-10\), then you get \(24 \ge 17\) and this is a true statement. Any other value of \(x\) less than or equal to \(-3\) may be used too, and you still get a true statement.
- Then calculate the left- and right-hand sides of the inequality \(-2x + 4 \ge -x {\,+\,}7\) when you substitute a value of \(x\) greater than or equal to \(-3\). For example, when you fill in \(x=10\), then you get \(-16 \ge -3\) and this is a false statement. Any other value of \(x\) greater than or equal to \(-3\) may be used too, and you still get a false statement.
- From these two numeric examples follows that solutions \(x\) of \(-2x + 4 \ge -x {\,+\,}7\) must satisfy \(x \le -3\).
The points where the inequality holds are shown in green in the number line below. An open circle around \(x=-3\) indicates that we are dealing with an inequality of the type \(\lt\) or \(\gt\), where in this case the point itself is not a solution. A closed circle indicates an inequality of the type \(\le\) or \(\ge\), and then the point marked on the number line is element of the solution set.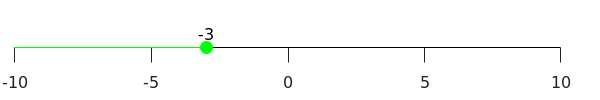
Unlock full access



